factoring advantages and disadvantages
Introduction
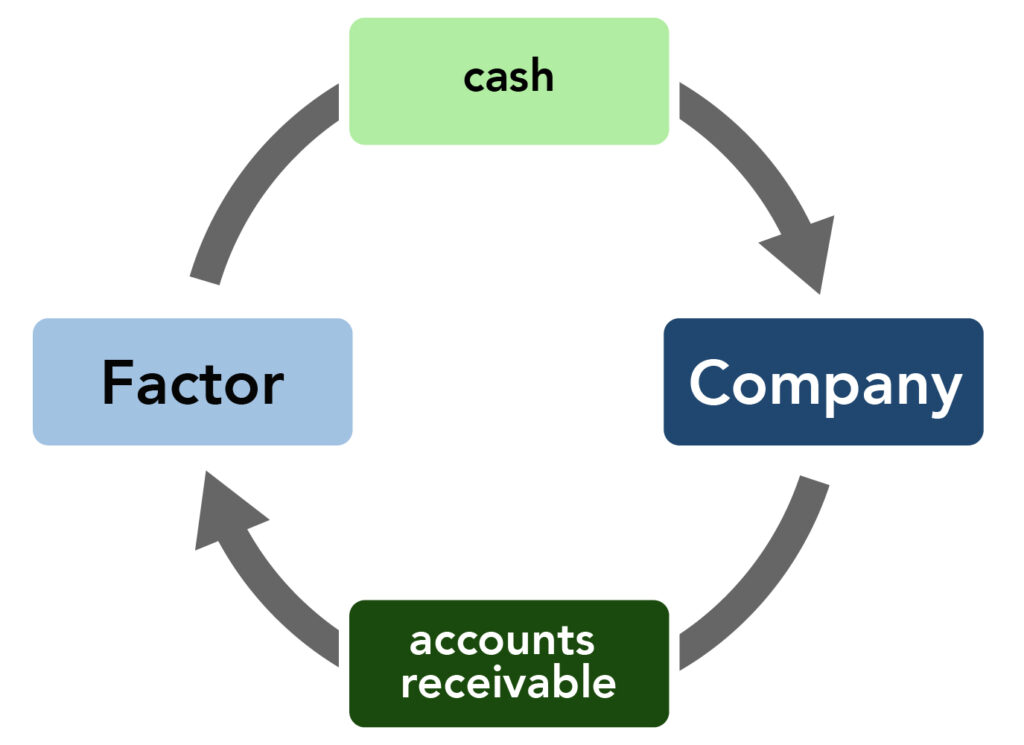
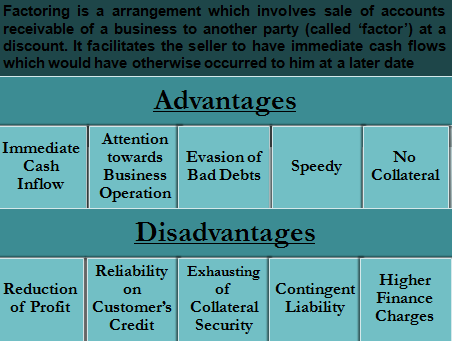
Factoring is a type of financial arrangement in which a company sells its accounts receivable to a third party, known as a factor, at a discounted rate in exchange for immediate cash. Factoring can be an attractive option for companies that need to improve their cash flow and access working capital quickly. However, as with any financial transaction, there are both advantages and disadvantages to factoring. In this article, we will explore the benefits and drawbacks of factoring for businesses.
Advantages of Factoring
- Improved cash flow: The most significant advantage of factoring is the immediate cash flow it provides. Companies can sell their accounts receivable to a factor and receive a large percentage of the value upfront, rather than waiting for payment from their customers. This can help businesses to cover their expenses, pay their employees, and invest in growth opportunities.
- Increased liquidity: Factoring can help businesses to increase their liquidity by converting their accounts receivable into cash. This can be especially important for companies that operate in industries with long payment cycles or that have large outstanding balances.
- No debt: Factoring is not a loan, so it does not create any debt for the business. Instead, the factor purchases the company’s accounts receivable at a discount, providing cash to the business without creating any additional liabilities.
- Access to credit: Factoring can be an attractive option for businesses that have been turned down for traditional bank loans or lines of credit. Factors typically do not require the same level of collateral or creditworthiness as banks, making it easier for businesses to access the financing they need.
- Outsourcing collections: Factoring companies typically handle the collections process for the accounts receivable they purchase. This can save businesses time and resources, as they no longer need to chase down late payments or manage collections themselves.
“Factoring”
refers to a mathematical process in which an expression is broken down into simpler parts, typically by finding its factors. For example, the expression x^2 – 4x can be factored into (x – 2)(x + 2).
“Debt factoring”
is a financial practice in which a company sells its accounts receivable (i.e., money owed to the company by customers) to a third-party, typically a financial institution called a factor. The factor then collects the debts from the customers and pays the company a percentage of the value of the debts, minus a fee.
Advantages of debt factoring can include improved cash flow, reduced administrative burden, and access to financing without having to borrow money. Disadvantages can include reduced profitability due to the fee charged by the factor, potential damage to customer relationships, and loss of control over the debt collection process.
“Disadvantages of factoring in business”
likely refers to the potential downsides of debt factoring, as discussed above.
“Benefits of factoring in financial services”
could refer to the advantages of debt factoring for financial institutions, such as generating revenue from the fees charged to companies for the service and gaining access to a pool of assets to invest.
“Advantages and disadvantages of factoring quadratic equations”
refers to the mathematical process of factoring quadratic expressions (i.e., expressions of the form ax^2 + bx + c) into simpler parts. Advantages of factoring quadratic equations can include simplifying calculations and solving certain types of equations. Disadvantages could include the complexity of some expressions, which can make factoring difficult or impossible.
“Disadvantages of debt factoring”
likely refers to the downsides of debt factoring, as discussed in point 2.
“Merits and demerits of factoring class 11”
likely refers to a discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of debt factoring in a high school or college-level math or business class.
“Types of factoring”
can refer to different variations of debt factoring, such as recourse factoring (in which the company retains some responsibility for collecting the debts) and non-recourse factoring (in which the factor assumes all responsibility for collecting the debts). Other types of factoring could include invoice factoring, spot factoring, and reverse factoring.
Disadvantages of Factoring
- Cost: Factoring can be an expensive form of financing, as factors typically charge fees and interest rates that are higher than traditional bank loans. However, the cost of factoring can be offset by the improved cash flow and access to working capital that it provides.
- Loss of control: When a company sells its accounts receivable to a factor, it loses control over the collections process. Factors may use aggressive tactics to collect payments, which can damage the business’s relationships with its customers.
- Risk of fraud: Factoring carries a risk of fraud, as some businesses may try to sell fake or fraudulent accounts receivable to factors. This can result in significant financial losses for the factor, as well as damage to its reputation.
- Potential damage to credit rating: If a business is unable to pay back the factor, it may damage its credit rating and make it more difficult to access financing in the future.
- Limited availability: Factoring may not be available to all businesses, as factors typically only purchase accounts receivable that are from creditworthy customers. This can limit the financing options available to businesses that operate in industries with high-risk customers.
What is factoring and its advantages?
Factoring is a financial transaction in which a business sells its accounts receivable (invoices) to a third party at a discount to raise capital. Factoring allows businesses to convert their accounts receivable into cash quickly, which can help improve their cash flow and provide funds to invest in growth opportunities. The advantages of factoring include improved cash flow, reduced administrative burden, and reduced risk of bad debt.
What are factoring limitations?
There are several limitations to factoring, including the fact that it can be expensive, as the factor will charge a fee for the service. Additionally, factoring may not be suitable for all types of businesses or industries, as some industries may have longer payment terms or higher rates of bad debt, which can make factoring less effective.
What is the disadvantage of factoring accounts receivable?
The main disadvantage of factoring accounts receivable is the cost. Factors typically charge a fee, which can range from 1-5% of the total value of the accounts receivable, depending on the creditworthiness of the customers and the amount of risk involved. This can be a significant cost for businesses, especially those with low-profit margins.
What are the risks of factoring?
One of the main risks of factoring is the possibility of bad debt. If a customer fails to pay their invoice, the business may still be responsible for repaying the factor. Additionally, the factor may require the business to provide a personal guarantee or collateral, which can put the business owner’s personal assets at risk. Finally, if the factor does not properly manage the collections process, it can damage the business’s relationship with its customers.
What is factoring?
Factoring is the process of finding the factors of a given number or algebraic expression. It is a fundamental concept in mathematics and has applications in cryptography, finance, and other areas.
What are the advantages of factoring?
- Divisibility: Factoring allows us to determine whether a number is divisible by a smaller number, which can be useful in simplifying calculations or solving problems.
- Simplification: Factoring can simplify algebraic expressions, making them easier to work with and manipulate.
- Cryptography: Factoring large numbers is used in cryptography, which is essential for secure communication and digital transactions.
- Finance: Factoring can be used in finance to convert accounts receivable into cash, allowing businesses to meet their financial obligations.
What are the disadvantages of factoring?
- Time-consuming: Factoring can be a time-consuming process, especially for large numbers or complex algebraic expressions.
- Complexity: Some numbers and expressions are difficult to factor, requiring advanced techniques and specialized knowledge.
- Limited application: Factoring has limited applications in certain fields and may not be useful in certain contexts.
- Insecurity: In the context of cryptography, the ability to factor large numbers can be used to break encryption schemes, making it essential to use sufficiently large prime numbers that cannot be factored easily.
How can factoring be used in cryptography?
Factoring large numbers is used in cryptography to create secure communication channels and digital transactions. The security of many encryption schemes relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers, making it an essential component of modern cryptography. However, the development of more powerful computers and mathematical techniques has made some encryption schemes vulnerable to attack, highlighting the importance of using sufficiently large prime numbers that cannot be factored easily.
Conclusion
Factoring can be an attractive option for businesses that need to improve their cash flow and access working capital quickly. However, as with any financial transaction, there are both advantages and disadvantages to factoring. Companies that are considering factoring should carefully weigh the benefits and drawbacks before making a decision. While factoring can provide immediate cash flow and increased liquidity, it can also be expensive and carry risks such as loss of control, potential fraud, and damage to credit rating. Ultimately, businesses should choose the financing option that best meets their needs and helps them achieve their growth objectives